What are Operators and Types of Operators in C programming?
In C programming, operators are symbols that are used to perform operations on operands. They can be classified into several categories:
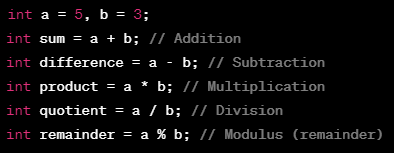
1. **Arithmetic Operators**: These operators are used to perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulus.
2. **Relational Operators**: Relational operators are used to compare two values. They return either true (1) or false (0).
```c
int a = 5, b = 3;
int result = a > b; // Greater than
result = a < b; // Less than
result = a >= b; // Greater than or equal to
result = a <= b; // Less than or equal to
result = a == b; // Equal to
result = a != b; // Not equal to
```
3. **Logical Operators**: These operators are used to perform logical operations like AND, OR, and NOT.
```c
int x = 1, y = 0;
int result = (x && y); // AND
result = (x || y); // OR
result = !x; // NOT
```
4. **Assignment Operators**: Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables.
```c
int a = 5;
a += 3; // Equivalent to a = a + 3;
a -= 2; // Equivalent to a = a - 2;
a *= 4; // Equivalent to a = a * 4;
a /= 2; // Equivalent to a = a / 2;
```
5. **Increment and Decrement Operators**: These operators are used to increment or decrement the value of a variable.
```c
int a = 5;
a++; // Increment a by 1
++a; // Increment a by 1
a--; // Decrement a by 1
--a; // Decrement a by 1
```
6. **Bitwise Operators**: Bitwise operators perform operations on individual bits of operands.
```c
int a = 5, b = 3;
int result = a & b; // Bitwise AND
result = a | b; // Bitwise OR
result = a ^ b; // Bitwise XOR
result = ~a; // Bitwise NOT
result = a << 1; // Left shift
result = a >> 1; // Right shift
```
These are some of the most commonly used operators in C programming. They allow you to manipulate data and control the flow of your program efficiently.





0 Comments